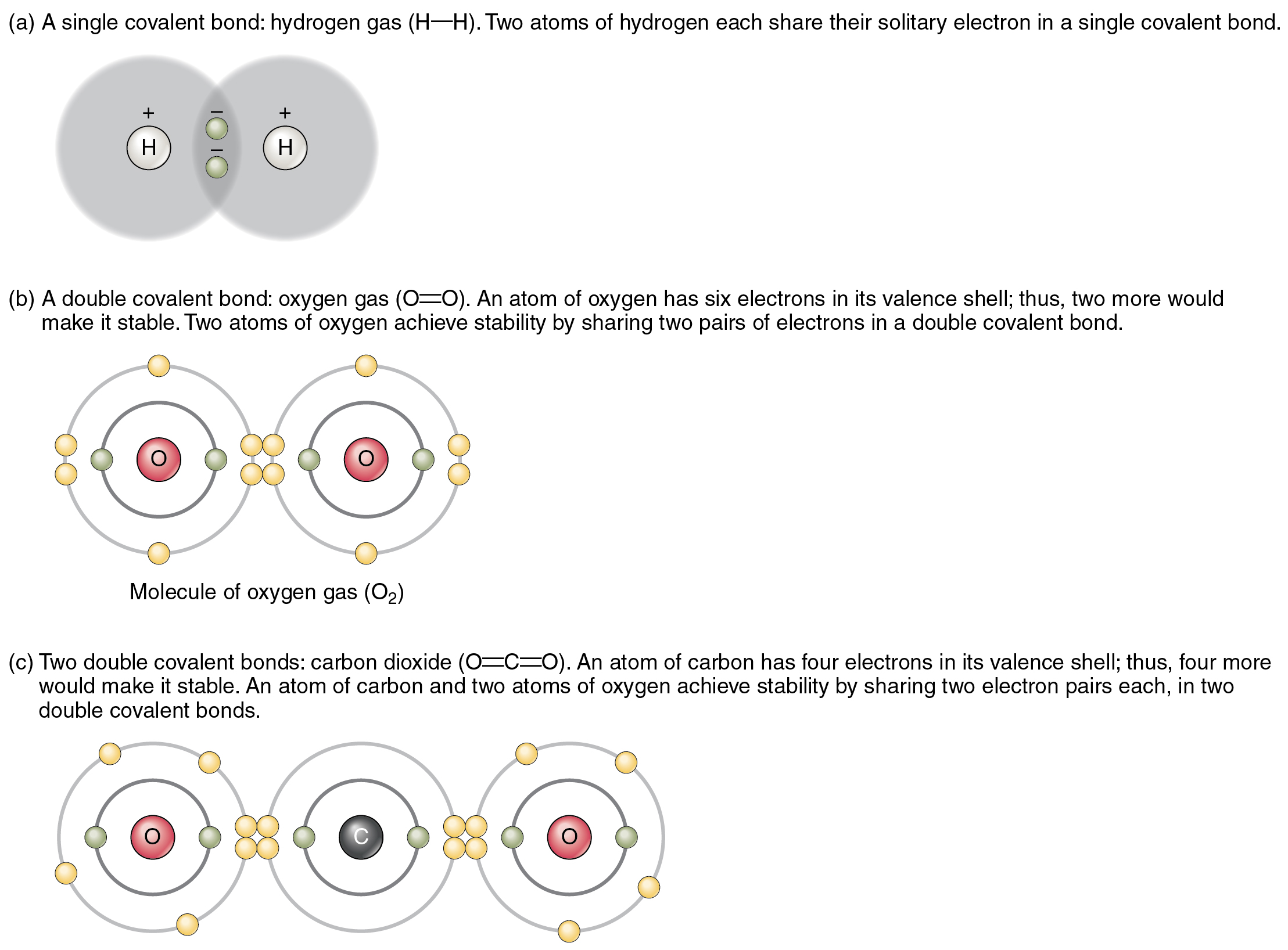
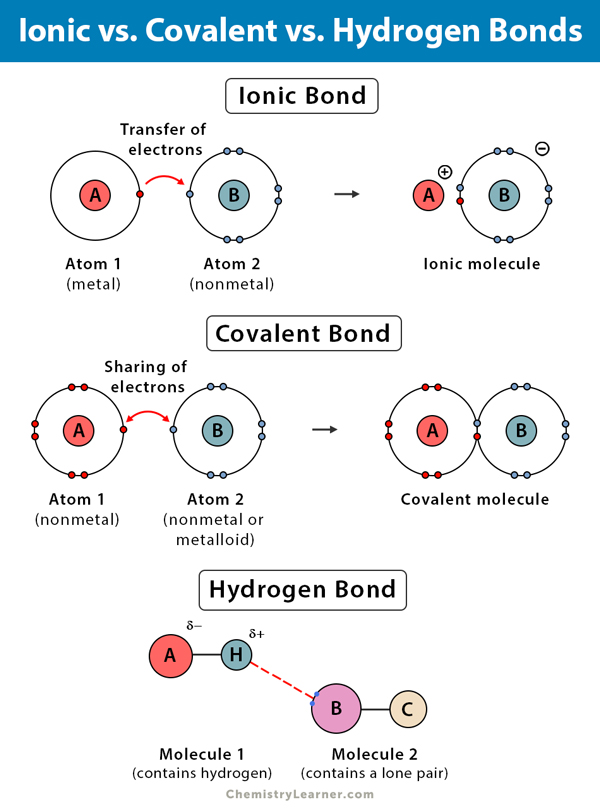
Does Hydrogen Form Ionic Bonds - Hydrogen bonds are intermolecular forces; Hydrogen bonds are intermolecular forces; These oppositely charged ions attract each other to form ionic. Covalent and ionic bonds are intramolecular forces. Covalent and ionic bonds are intramolecular forces. These are ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and hydrogen bonds. Recall that an atom typically has the same number of.
Covalent and ionic bonds are intramolecular forces. Hydrogen bonds are intermolecular forces; Hydrogen bonds are intermolecular forces; Recall that an atom typically has the same number of. These oppositely charged ions attract each other to form ionic. These are ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and hydrogen bonds. Covalent and ionic bonds are intramolecular forces.




.PNG)